The United Nations (UN) was formed in 1945 in the aftermath of World War II. The organization was established with the aim of preventing future conflicts and promoting international cooperation. The UN replaced the League of Nations, which had failed to prevent the outbreak of another devastating war. The UN Charter, a founding document that outlines the principles and objectives of the organization, was signed on June 26, 1945, by representatives of 50 countries. Today, the UN has 193 member states, making it the largest intergovernmental organization in the world.
The formation of the UN was a response to the horrors of war and a commitment to creating a more peaceful and just world. The organization’s main objectives, as stated in the UN Charter, include maintaining international peace and security, promoting human rights, fostering social and economic development, and providing a platform for member states to address global issues. The UN’s formation marked a significant shift in global governance, with nations recognizing the need for luna togel collective action and cooperation to tackle common challenges.
The UN’s headquarters is located in New York City, but it has offices and agencies in various parts of the world. The organization operates on the principle of sovereign equality, meaning that each member state has an equal voice and representation in decision-making processes. The UN’s structure and organization are designed to facilitate collaboration and consensus-building among member states.

Structure and Organization of the United Nations
The United Nations is composed of several key bodies and institutions that work together to fulfill its objectives. The main organs of the UN are the General Assembly, the Security Council, the Economic and Social Council, the Secretariat, and the International Court of Justice. Each of these organs has specific responsibilities and functions within the organization.
The General Assembly is the main deliberative body of the UN, consisting of representatives from all member states. It serves as a forum for member states to discuss and coordinate on a wide range of global issues. The General Assembly meets annually in regular sessions, where major decisions are made, and resolutions are adopted. Each member state has one vote in the General Assembly, ensuring equal representation.
The Security Council is responsible for maintaining international peace and security. It has 15 members, including five permanent members – China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States – and ten non-permanent members elected by the General Assembly for two-year terms. The Security Council has the power to impose sanctions, authorize military interventions, and establish peacekeeping missions. Its decisions are binding on all member states.
Challenges Facing the United Nations
The Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) focuses on promoting economic and social development. It is responsible for coordinating the UN’s work on economic, social, and environmental issues. ECOSOC has 54 member states elected by the General Assembly for three-year terms. It plays a crucial role in setting global development agendas and fostering international cooperation in areas such as poverty eradication, healthcare, education, and sustainable development.
The Secretariat is the administrative arm of the UN, headed by the Secretary-General. It supports the work of the other organs and implements their decisions. The Secretary-General is appointed by the General Assembly upon the recommendation of the Security Council. The Secretary-General serves as the chief administrative officer of the UN and acts as a diplomat and spokesperson for the organization. The Secretariat has various departments and offices that carry out specialized functions, such as peacekeeping, humanitarian assistance, and economic analysis.
The International Court of Justice (ICJ) is the principal judicial organ of the UN. It settles legal disputes between member states and provides advisory opinions on legal questions referred to it by authorized UN organs. The ICJ consists of 15 judges elected by the General Assembly and the Security Council for nine-year terms. Its decisions are binding and serve as an authoritative interpretation of international law.
The Main Functions and Objectives
The United Nations has a broad mandate to address global challenges and promote international cooperation. Its main functions and objectives can be summarized as follows:
- Maintaining International Peace and Security: One of the primary purposes of the UN is to prevent conflicts and maintain global peace and security. The organization achieves this through diplomatic negotiations, peacekeeping missions, and conflict resolution efforts. The Security Council, in particular, plays a crucial role in responding to threats to international peace and authorizing necessary measures to restore stability.
- Promoting Human Rights: The UN is committed to upholding and promoting human rights for all individuals. It has adopted several international agreements and declarations that set standards for the protection of human rights, such as the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. The UN works to monitor human rights situations, raise awareness, and provide assistance to countries in implementing human rights obligations.
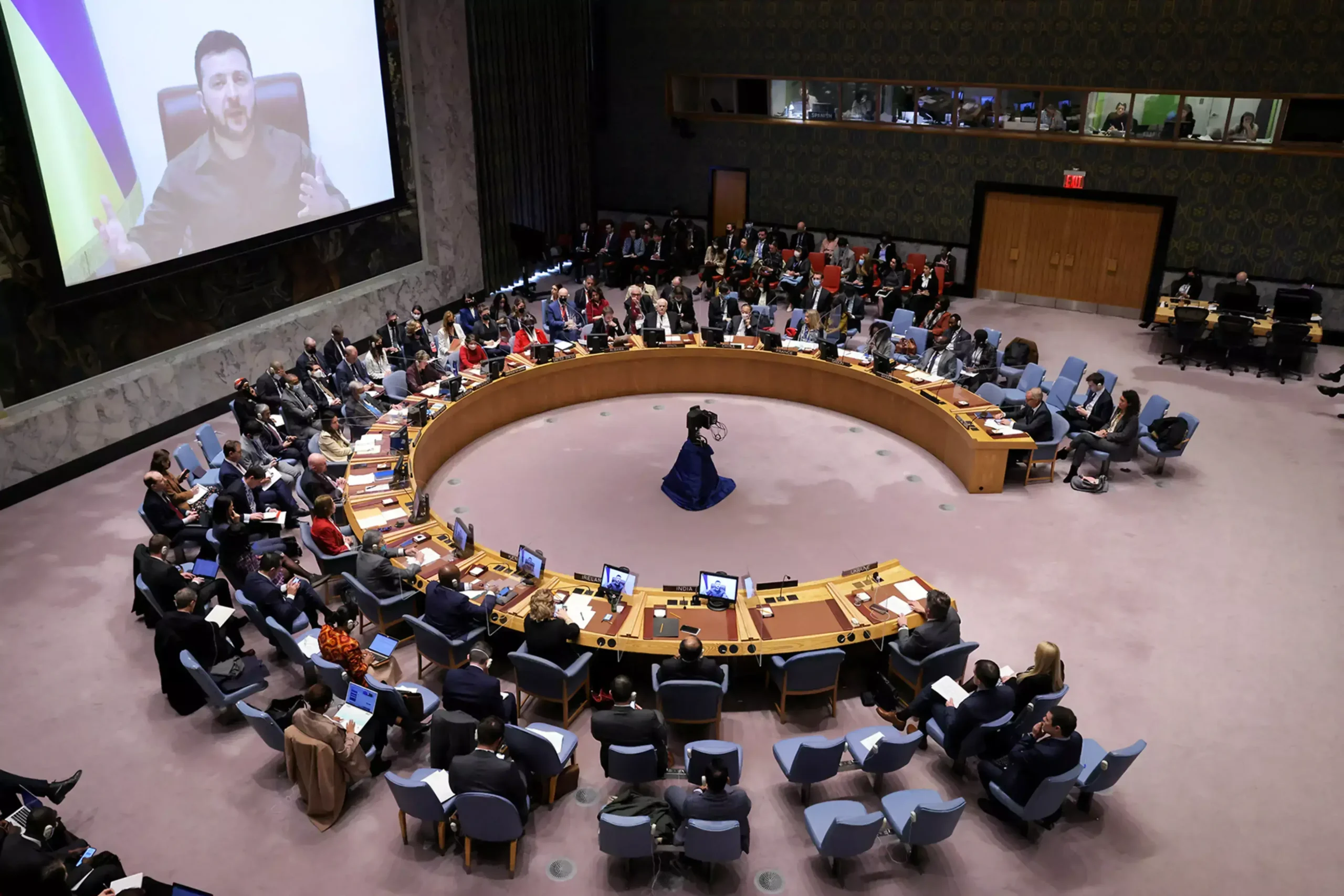

The Role of the United Nations in International Peace and Security
One of the primary responsibilities of the United Nations is to maintain international peace and security. The UN achieves this through various means, including preventive diplomacy, peacekeeping operations, and conflict resolution efforts.
Preventive diplomacy involves early intervention and mediation to prevent conflicts from escalating. The UN’s diplomatic channels and mediators work behind the scenes to facilitate dialogue and find peaceful solutions to disputes. By addressing the root causes of conflicts and promoting dialogue, the UN aims to prevent violence and protect vulnerable populations.
Peacekeeping operations are a crucial tool in the UN’s efforts to maintain peace and security. Peacekeepers, often deployed in conflict-affected regions, work to stabilize situations, protect civilians, and support peace processes. UN peacekeeping missions have been deployed in various parts of the world, including Africa, the Middle East, and the Balkans. These missions help create conditions for lasting peace and contribute to post-conflict reconstruction and development.
In addition to preventive diplomacy and peacekeeping, the UN plays a vital role in conflict resolution. The Security Council, as the primary organ responsible for addressing threats to international peace, has the authority to impose sanctions, authorize the use of force, and establish peacekeeping missions. The UN also supports peace processes and negotiations, facilitating dialogue between conflicting parties and providing technical assistance.
The UN’s role in international peace and security is essential in a world grappling with complex conflicts and emerging threats. By promoting dialogue, preventing conflicts, and facilitating peace processes, the UN contributes to the stability and well-being of nations.
The Efforts in Promoting Human Rights and Sustainable Development
The United Nations is committed to promoting and protecting human rights for all individuals. It recognizes the inherent dignity and equal rights of every person, regardless of their race, gender, religion, or nationality. The UN has adopted several international agreements and declarations that outline the fundamental rights and freedoms that should be enjoyed by all.
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights, adopted by the UN General Assembly in 1948, is a landmark document that sets out a common standard of achievements for all peoples and all nations. It encompasses civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights, and serves as a guiding principle in the promotion of human rights worldwide. The UN, through its human rights bodies and mechanisms, monitors the implementation of human rights obligations and investigates allegations of human rights violations.
United Nations Agencies and Programs
The United Nations has a vast network of specialized agencies, programs, and funds that work to address specific issues and provide targeted support. These agencies operate under the umbrella of the UN and collaborate with member states, civil society organizations, and other partners to achieve common objectives.
One of the most well-known UN agencies is the World Health Organization (WHO), which is responsible for promoting global health and coordinating responses to health emergencies. The WHO works to prevent and control diseases, improve access to healthcare, and promote health equity. It provides technical assistance, conducts research, and sets health standards and guidelines.
Another important UN agency is the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). UNESCO aims to promote peace and sustainable development through education, science, culture, and communication. It coordinates international cooperation in areas such as education, cultural heritage preservation, media development, and scientific research.

Major Achievements and Challenges of the United Nations
Since its establishment, the United Nations has achieved significant milestones in its efforts to promote peace, human rights, and development. Some of the major achievements of the UN include:
- Peacekeeping: The UN has successfully deployed peacekeeping missions in various conflict-affected regions, helping to stabilize situations, protect civilians, and facilitate peace processes. Peacekeeping efforts in countries like Namibia, El Salvador, and Mozambique have been instrumental in bringing an end to conflicts and laying the foundation for peace and development.
- Human Rights: The UN has played a crucial role in advancing human rights globally. The adoption of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and the establishment of human rights mechanisms have contributed to the recognition and protection of human rights in many countries. The UN’s human rights bodies, such as the Human Rights Council and the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, monitor human rights situations and advocate for their improvement.
- Sustainable Development: The UN’s commitment to sustainable development is exemplified by the adoption of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the SDGs. These global frameworks have mobilized efforts to eradicate extreme poverty, combat climate change, and promote sustainable economic growth. The UN’s work in areas such as education, healthcare, and environmental protection has made significant progress towards achieving sustainable development goals.
Overcoming these challenges requires ongoing commitment, collaboration, and reform within the UN and among member states. The organization’s ability to adapt and evolve will be crucial in effectively addressing the complex global issues of the 21st century.