Cancer Treatment remains one of the most formidable challenges in the medical field. Despite significant advancements, it continues to affect millions of people worldwide. However, ongoing research and technological innovations have led to the development of various treatment modalities aimed at improving survival rates and enhancing the quality of life for cancer patients. This article explores the different types of cancer treatments, recent advancements, challenges, and future prospects in the fight against cancer.

Contents
Understanding Cancer
Cancer is a complex group of diseases characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells. If not treated, these cells can invade nearby tissues and organs, leading to severe health complications and death. The causes of cancer are multifactorial, including genetic predisposition, environmental factors, lifestyle choices, and infections.
Types of Cancer Treatments
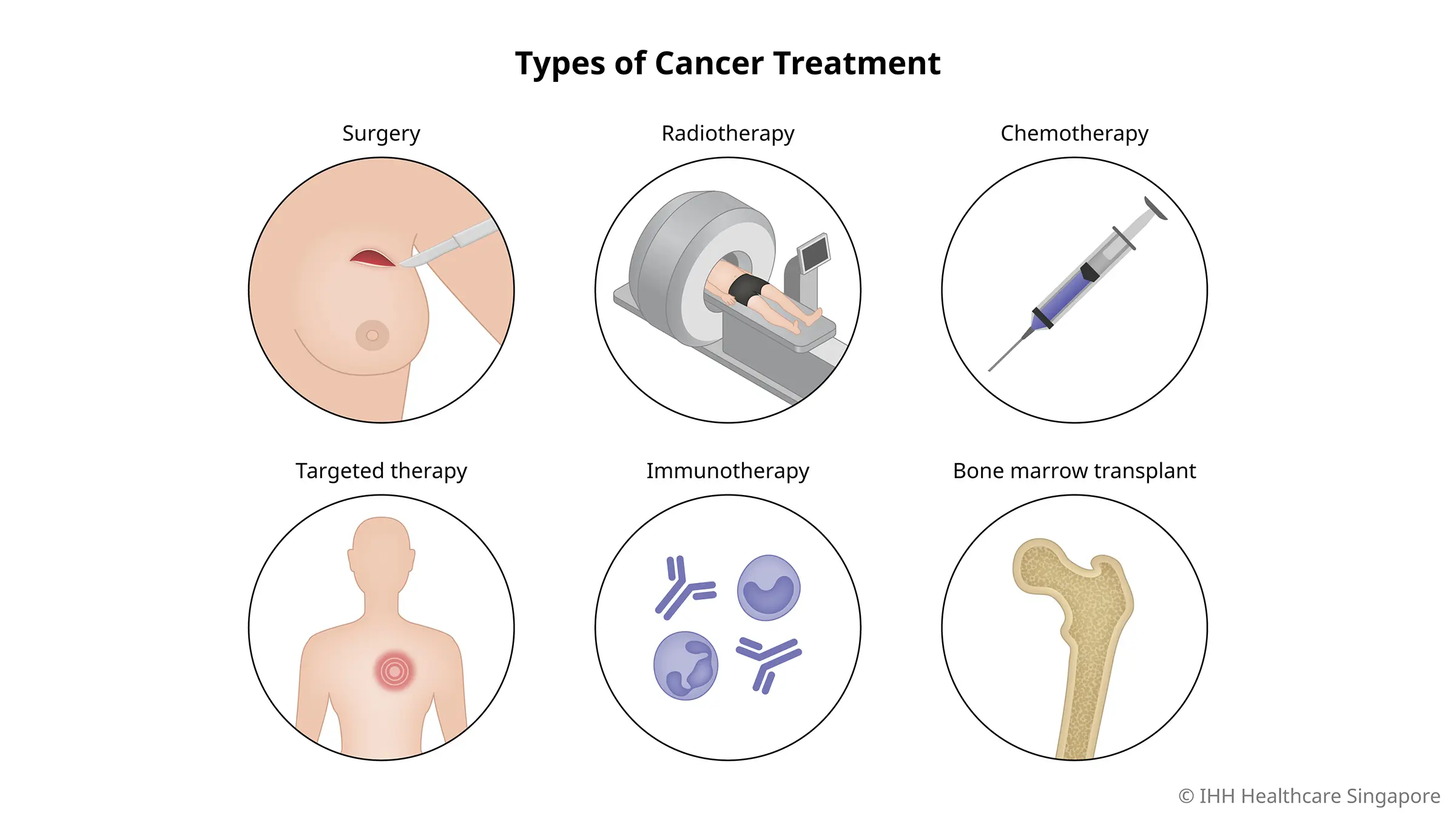
Cancer treatment aims to eliminate cancer cells, prevent their spread, and reduce symptoms. The choice of treatment depends on the type and stage of cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. Here are the primary types of cancer treatments:
1. Surgery
Surgery involves the physical removal of cancerous tissues from the body. It is often the first line of treatment for many solid tumors. Surgical techniques have evolved, with minimally invasive procedures such as laparoscopy and robotic surgery offering reduced recovery times and fewer complications.
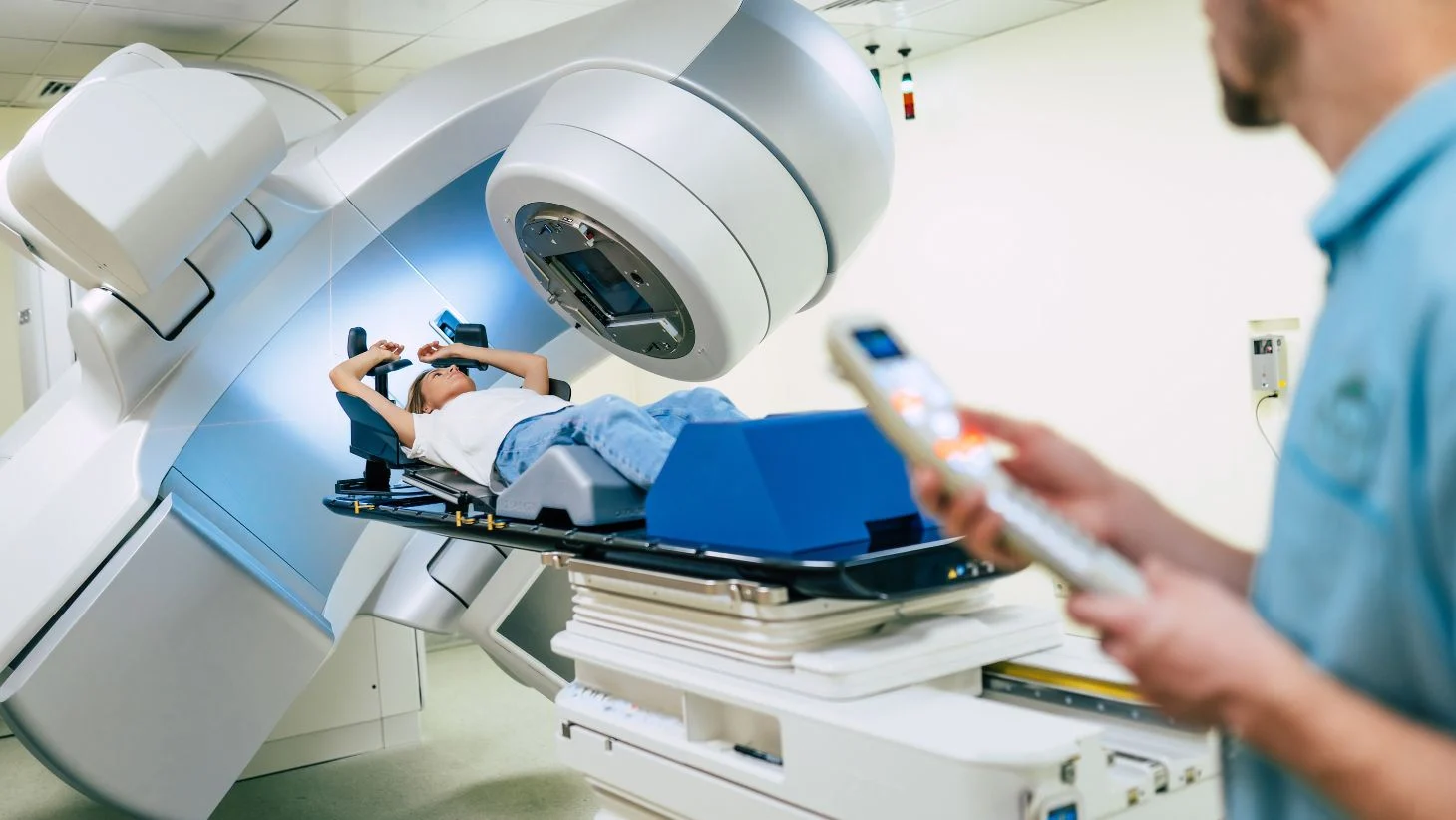
2. Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy particles or waves, such as X-rays, gamma rays, or proton beams, to destroy or damage cancer cells. It can be used alone or in combination with other treatments. Advanced techniques like intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) allow for more precise targeting of tumors, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
3. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill or inhibit the growth of cancer cells. These drugs can be administered orally, intravenously, or through other routes. While effective, chemotherapy often comes with significant side effects, such as nausea, fatigue, and immune suppression, due to its impact on healthy cells.
4. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy leverages the body’s immune system to fight cancer. It includes treatments like checkpoint inhibitors, which block proteins that prevent immune cells from attacking cancer cells, and CAR-T cell therapy, which involves modifying a patient’s T cells to better target cancer. Immunotherapy has shown remarkable success in treating certain types of cancer, such as melanoma and lung cancer.
5. Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy involves drugs that specifically target molecular changes in cancer cells that drive their growth and survival. These therapies aim to interfere with specific pathways or proteins involved in cancer progression, offering a more personalized approach to treatment. Examples include tyrosine kinase inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies.
6. Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy is used to treat cancers that are sensitive to hormones, such as breast and prostate cancer. It works by blocking the body’s ability to produce hormones or by interfering with their effects on cancer cells. This therapy can help slow or stop the growth of hormone-dependent tumors.
7. Stem Cell Transplant
Stem cell transplants, also known as bone marrow transplants, involve replacing damaged or destroyed bone marrow with healthy stem cells. This procedure is often used for blood cancers, such as leukemia and lymphoma. Stem cell transplants can be autologous (using the patient’s own cells) or allogeneic (using donor cells).
Recent Advancements in Cancer Treatment
The field of oncology has seen significant advancements in recent years, driven by technological innovations and a deeper understanding of cancer biology. Some of the notable advancements include:
1. Precision Medicine
Precision medicine tailors treatment to the individual characteristics of each patient and their cancer. This approach involves genetic profiling of tumors to identify specific mutations and tailor treatments that target those mutations. Precision medicine has led to the development of targeted therapies and improved treatment outcomes for many patients.
2. Liquid Biopsies
Liquid biopsies are a non-invasive method for detecting cancer-related genetic mutations and monitoring treatment response. By analyzing circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in a patient’s blood, liquid biopsies provide real-time information about the tumor’s genetic makeup, enabling more accurate and timely adjustments to treatment plans.
3. Immunotherapy Breakthroughs
The success of immunotherapies, such as checkpoint inhibitors and CAR-T cell therapy, has revolutionized cancer treatment. These therapies have shown durable responses and long-term survival benefits in patients with advanced cancers, offering new hope for those with previously untreatable tumors.
4. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Oncology
AI and machine learning are being togelon increasingly utilized in cancer research and treatment. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict treatment responses, and assist in the development of new therapies. AI is also being used to improve diagnostic accuracy and personalize treatment plans.
5. Advances in Radiotherapy
New radiotherapy techniques, such as proton therapy and MRI-guided radiotherapy, provide more precise targeting of tumors while sparing healthy tissues. These advancements have improved the effectiveness of radiation therapy and reduced side effects, enhancing the quality of life for patients.
Challenges in Cancer Treatment

Despite the progress, several challenges remain in the fight against cancer:
- Resistance to Treatment: Cancer cells can develop resistance to therapies, leading to treatment failure and disease progression. Understanding and overcoming resistance mechanisms is a major focus of ongoing research.
- Side Effects: Many cancer treatments come with significant side effects that can impact a patient’s quality of life. Developing therapies that are both effective and less toxic is a critical goal.
- Access to Care: There are disparities in access to cancer care, with patients in low- and middle-income countries often lacking access to advanced treatments. Addressing these disparities is essential to ensure equitable care for all patients.
- Cost of Treatment: The high cost of cancer treatment, particularly for newer therapies like immunotherapy and targeted therapy, can be a barrier for many patients. Efforts to reduce costs and improve affordability are needed.
Future Prospects in Cancer Treatment
The future of cancer treatment holds promise with ongoing research and technological advancements. Key areas of focus include:
- Combination Therapies: Combining different types of treatments, such as immunotherapy and targeted therapy, has the potential to improve outcomes and overcome resistance. Ongoing clinical trials are exploring various combination approaches.
- Personalized Vaccines: Cancer vaccines designed to target specific antigens present on a patient’s tumor cells are being developed. These vaccines aim to stimulate the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively.
- Gene Editing: Technologies like CRISPR-Cas9 offer the potential to edit genes associated with cancer, providing new avenues for treatment. Gene editing could be used to repair faulty genes or enhance the immune system’s ability to fight cancer.
- Early Detection: Advances in early detection methods, such as liquid biopsies and advanced imaging techniques, can improve the chances of successful treatment by identifying cancer at its earliest stages.
- Nanotechnology: Nanoparticles are being explored as a means to deliver drugs directly to cancer cells, increasing the effectiveness of treatments and reducing side effects. Nanotechnology also holds promise for early detection and imaging.
Conclusion
Cancer treatment has come a long way, with significant advancements improving survival rates and quality of life for many patients. From traditional methods like surgery and radiation therapy to innovative approaches like immunotherapy and precision medicine, the landscape of cancer treatment is continually evolving. While challenges remain, ongoing research and technological innovations offer hope for even more effective and accessible treatments in the future. As we continue to advance our understanding of cancer and develop new therapies, the goal of achieving better outcomes and ultimately finding a cure becomes increasingly attainable.
Read More Article About “Keajaiban Goa Gong: Destinasi Wisata Alam di Pacitan“