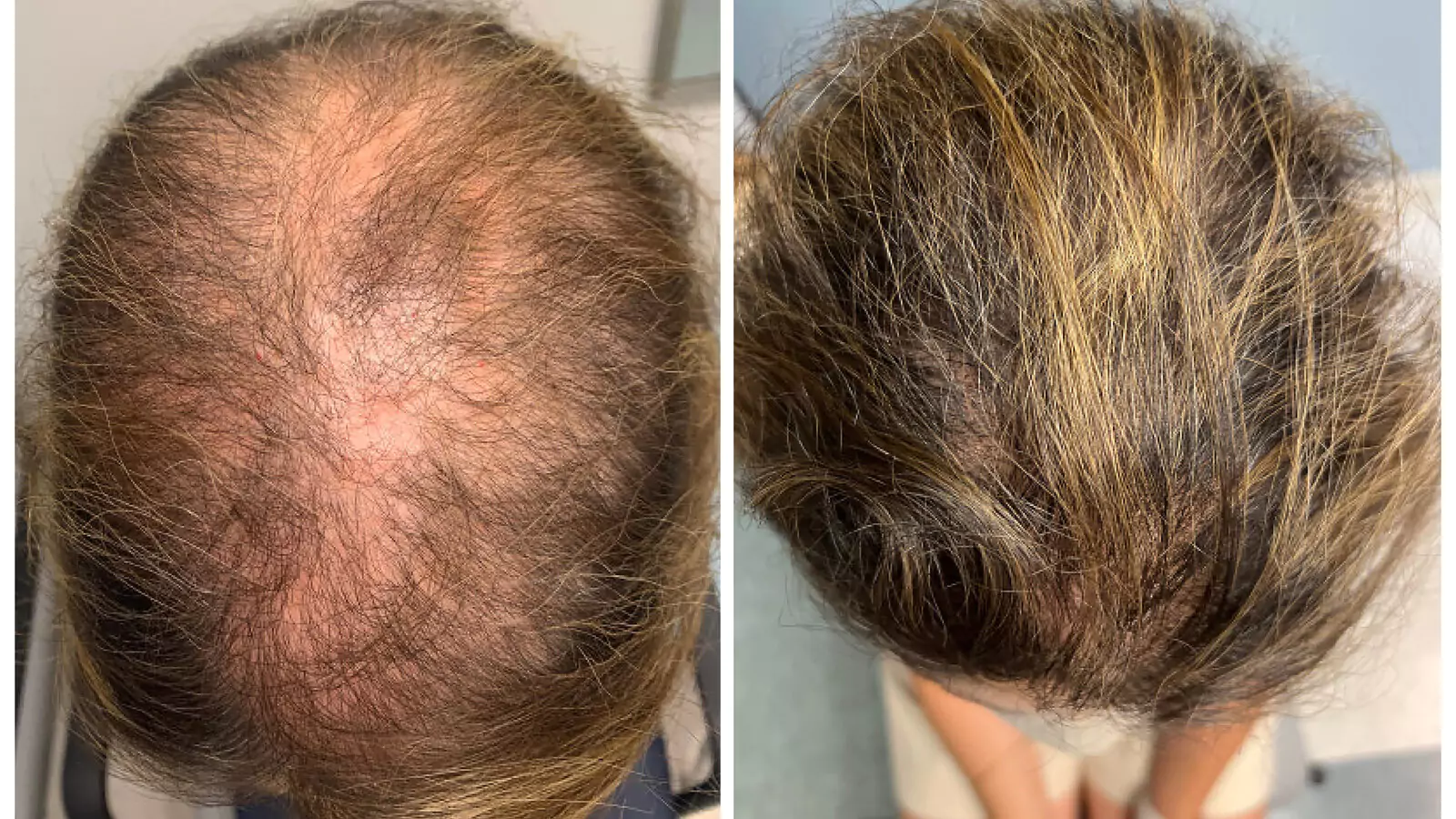
In the quest to comprehend the complexities of hair loss, it is imperative to embark on a journey that delves into the depths of both the physiological and psychological facets of this condition. The phenomenon, often perceived merely as a cosmetic inconvenience, transcends superficial concerns, touching upon aspects of health, identity, and emotional well-being. This guide aims to shed light on the multifaceted nature of hair loss, offering a beacon of knowledge for those navigating through its murky waters.
Embarking on this exploration requires a foundational understanding of what constitutes normal hair growth and shedding. The human scalp, a tapestry woven with approximately 100,000 hair follicles, experiences a continuous cycle of jpslot growth, rest, and shedding. It’s a natural process for individuals to shed between 50 to 100 hairs daily, a fact that often goes unnoticed due to the simultaneous growth of new strands. However, when the balance between shedding and growth is disrupted, individuals begin to perceive the tangible reality of hair loss.
This preliminary insight sets the stage for a deeper investigation into the types, causes, and treatments associated with hair loss. By approaching this topic with a scientific lens, we aim to dispel myths, offer solace through understanding, and navigate the path towards effective solutions. Let us journey together through the intricate landscape of hair loss, armed with knowledge and compassion.
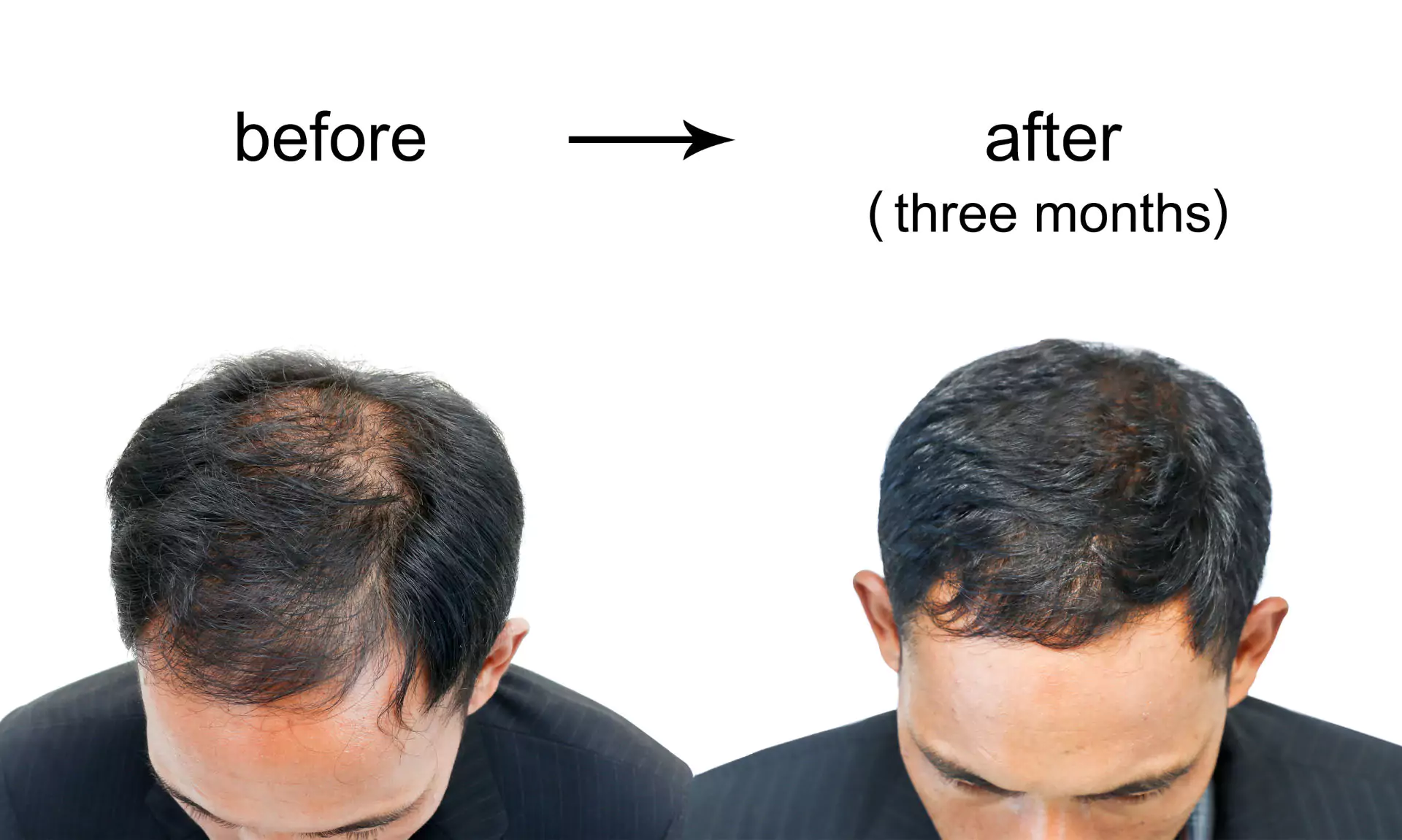
Contents
- 1 Types of Baldness
- 2 Causes of Baldness
- 3 The science behind hair growth
- 4 Common myths about hair loss
- 5 Signs and symptoms of hair loss
- 6 Diagnosing hair loss – how to know if you’re losing your hair
- 7 Hair loss treatments and solutions
- 8 Natural remedies for hair loss
- 9 Lifestyle changes to prevent hair loss
- 10 Coping with hair loss – emotional and psychological aspects
- 11 When to seek professional help for hair loss
- 12 Hair loss prevention tips
- 13 Conclusion
- 14 Author
Types of Baldness
Delving into the taxonomy of Baldness unveils a diversity of types, each with unique characteristics and underlying causes. Alopecia, the medical term for hair loss, manifests in various forms, painting a complex picture of this widespread condition. Among the most prevalent types is Androgenetic Alopecia, known colloquially as male or female pattern baldness. This variant, deeply rooted in genetic predispositions, exhibits a predictable pattern of hair thinning and loss, predominantly affecting the crown and frontal hairline in men, and diffuse thinning across the scalp in women.
Another notable type is Alopecia Areata, an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to round patches of Baldness. This condition can evolve into more extensive forms, such as Alopecia Totalis and Alopecia Universalis, culminating in the loss of all scalp hair or all body hair, respectively. The unpredictability and potential severity of Alopecia Areata underscore the complex interplay between genetics, immunity, and hair health.
Telogen Effluvium presents a different scenario, characterized by widespread thinning of the hair due to an increased number of hairs entering the resting phase. Triggered by stress, hormonal imbalances, or medical conditions, this type of Baldness underscores the significance of external and internal factors in hair health. Each type of hair loss, with its distinct features and triggers, contributes to the intricate tapestry of this condition, demanding a nuanced approach to diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of Baldness
Unraveling the enigma of Baldness necessitates an examination of the myriad causes that precipitate its onset. The etiology of Baldness is a complex interplay of genetic, hormonal, environmental, and lifestyle factors, each contributing to the weakening of hair follicles and subsequent Baldness. At the genetic level, a predisposition to certain types of hair loss, such as Androgenetic Alopecia, sets the stage for the condition’s development, influenced further by hormonal fluctuations, particularly those involving dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone.
Environmental factors, including exposure to pollutants and toxins, can exacerbate the vulnerability of hair follicles, leading to their premature aging and dysfunction. Similarly, nutritional deficiencies, lacking essential vitamins and minerals, impede the ability of hair to grow and thrive. Stress, both physical and emotional, has been identified as a catalyst for conditions like Telogen Effluvium, where a significant stress event can shift hair follicles into the resting phase, culminating in noticeable Baldness months later.
Lifestyle choices, encompassing diet, exercise, and hair care practices, also play a pivotal role in hair health. Poor dietary habits can deprive the body of the nutrients necessary for robust hair growth, while excessive styling and harsh chemical treatments can inflict direct damage on hair follicles. Recognizing the multifaceted causes of Baldness is paramount in crafting effective prevention and treatment strategies, tailored to address the unique circumstances of each individual.

The science behind hair growth
To navigate the complexities of Baldness, one must first understand the science underpinning hair growth. The lifecycle of a hair strand is a testament to the dynamic nature of hair, encompassing three distinct phases: anagen (growth), catagen (transition), and telogen (resting). The anagen phase, lasting between two to six years, signifies a period of active growth, during which hair follicles push out new strands. This phase is succeeded by the catagen phase, a brief transitional period where growth ceases and the hair prepares to enter the resting state.
The telogen phase marks a time of dormancy, lasting approximately three months, after which the hair strand falls out, making way for new growth. This cyclical process is influenced by various factors, including genetics, hormones, and overall health, dictating the rate of hair growth and its eventual shedding. Disruptions in this cycle, triggered by stress, hormonal imbalances, or disease, can lead to premature hair loss, underscoring the delicate balance required for healthy hair growth.
Understanding the mechanisms of hair growth provides a foundation for addressing Baldness, enabling individuals to identify deviations from normal growth patterns and seek appropriate interventions. It is through this scientific lens that we can begin to demystify the process of Baldness, approaching it with informed strategies for prevention and treatment.
Common myths about hair loss
The discourse surrounding Baldness is rife with myths and misconceptions, clouding the understanding of this condition with unfounded beliefs. One of the most pervasive myths is the notion that frequent hat wearing contributes to hair loss. This belief, rooted in the idea that hats restrict blood flow to the scalp, lacks scientific evidence, as hair loss is primarily influenced by genetic and hormonal factors rather than external pressure on the scalp.
Another common misconception is the idea that Baldness is solely a male concern. While it’s true that men are more likely to experience visible balding, women also face significant challenges with hair thinning and loss, often manifesting in less noticeable but equally distressing ways. This misconception perpetuates a gender bias in discussions about hair loss, obscuring the universality of the condition.
The belief that stress is a minor factor in hair loss also warrants scrutiny. While stress alone may not cause permanent hair loss, it can trigger conditions like Telogen Effluvium, leading to significant, albeit temporary, hair shedding. Disentangling fact from fiction is crucial in fostering a comprehensive understanding of hair loss, guiding individuals towards evidence-based perceptions and solutions.
Signs and symptoms of hair loss
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of Baldness is the first step in addressing this condition proactively. The manifestations of hair loss vary, ranging from gradual thinning on the top of the head, common in both men and women, to circular or patchy bald spots, often indicative of Alopecia Areata. Some individuals may experience sudden loosening of hair, a phenomenon that can result in handfuls of hair coming out when washing or gently tugging at the strands.
Observing changes in the hairline, particularly in men, can provide early indications of Androgenetic Alopecia. Women may notice a broadening of the part in their hair, signaling diffuse thinning. Additionally, full-body hair loss, a rare but concerning symptom, can occur as a result of medical treatments such as chemotherapy.
Paying attention to these signs and symptoms, while also monitoring for scalp irritations such as redness, scaling, or pain, can facilitate early intervention. Early recognition and diagnosis are pivotal in mitigating the progression of Baldness, empowering individuals to seek timely treatment options.
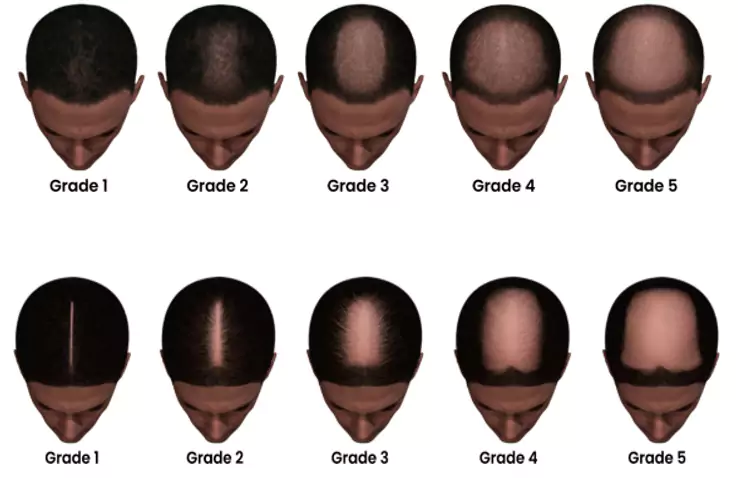
Diagnosing hair loss – how to know if you’re losing your hair
Diagnosing hair loss involves a multifaceted approach, incorporating clinical examination, personal history, and, in some cases, diagnostic tests. A healthcare provider, often a dermatologist specializing in skin and hair conditions, will begin by assessing the pattern and extent of Baldness, inquiring about family history, and discussing any relevant lifestyle factors or stressors. This initial evaluation aims to differentiate between the various types of Baldness, identifying potential underlying causes.
Scalp examination plays a crucial role in the diagnostic process, enabling the identification of disorders that may contribute to hair loss, such as scalp dermatitis or psoriasis. In instances where the cause of hair loss is unclear, a scalp biopsy may be conducted, involving the removal of a small section of scalp tissue for microscopic analysis. Blood tests are another diagnostic tool, useful in detecting hormonal imbalances, nutritional deficiencies, or signs of autoimmune disorders.
Armed with a comprehensive understanding of the individual’s hair loss, healthcare providers can formulate a targeted treatment plan. Recognizing the signs and seeking professional evaluation are essential steps in navigating the path towards managing hair loss effectively.
Hair loss treatments and solutions
The landscape of hair loss treatments and solutions is vast, offering a spectrum of options tailored to different types and causes of Baldness. For individuals grappling with Androgenetic Alopecia, medications such as Minoxidil (Rogaine) and Finasteride (Propecia) have emerged as cornerstones of treatment, proven to slow Baldness and, in some cases, stimulate regrowth. Minoxidil, a topical solution, enhances hair follicle activity, while Finasteride, an oral medication, targets hormonal factors by inhibiting the production of DHT.
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) presents a non-invasive alternative, utilizing light energy to stimulate hair growth and enhance the health of existing hair. Hair transplantation surgery, although more invasive, offers a permanent solution for those with significant hair loss, involving the transfer of hair follicles from dense to thinning areas of the scalp.
Beyond medical interventions, lifestyle modifications, including a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, adequate hydration, and stress management, play a crucial role in supporting hair health. Embracing a holistic approach to hair loss treatment, combining medical, lifestyle, and supportive measures, can optimize outcomes and improve quality of life for those affected by hair loss.
Natural remedies for hair loss
In the quest for hair loss solutions, natural remedies have garnered attention for their potential to support hair health with minimal side effects. Essential oils, such as rosemary and peppermint, have been studied for their ability to stimulate hair growth through increased blood circulation to the scalp. Scalp massages, utilizing these oils or performed on their own, offer a dual benefit of promoting relaxation and enhancing hair follicle stimulation.
Dietary supplements, including biotin, zinc, and iron, address nutritional gaps that may contribute to hair loss. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before embarking on supplementation, ensuring compatibility with individual health profiles and avoiding potential interactions with existing medications.
Herbal remedies, such as saw palmetto, have also been explored for their role in managing Baldness, particularly in cases linked to hormonal imbalances. While the efficacy of natural remedies varies, integrating them into a comprehensive hair care routine, in consultation with healthcare professionals, can offer supportive benefits in the management of hair loss.
Lifestyle changes to prevent hair loss
Preventing hair loss extends beyond medical interventions, encompassing lifestyle changes that nurture hair health from the inside out. A balanced diet, rich in proteins, vitamins, and minerals, lays the foundation for strong, healthy hair. Incorporating foods high in iron, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids can fortify hair growth and resilience.
Regular exercise, by improving overall health and reducing stress, indirectly supports hair health. Stress reduction techniques, such as meditation, yoga, and mindful breathing, can mitigate the impact of stress-related hair loss, emphasizing the interconnectedness of mental and physical well-being.
Hair care practices also play a pivotal role in preventing Baldness. Minimizing the use of harsh chemicals, reducing the frequency of heat styling, and adopting gentle hair handling techniques can alleviate stress on hair follicles, preserving hair integrity. Embracing these lifestyle changes, rooted in a holistic approach to health and well-being, can significantly contribute to the prevention of hair loss.
Coping with hair loss – emotional and psychological aspects
Hair loss transcends physical appearance, deeply affecting emotional and psychological well-being. The experience of losing hair can evoke feelings of distress, diminished self-esteem, and social anxiety, highlighting the need for compassionate support and coping strategies. Engaging in open conversations with friends, family, or support groups can offer solace, providing a platform for shared experiences and emotional validation.
Seeking professional counseling or therapy can be beneficial in navigating the complex emotions associated with Baldness, offering tools for building resilience and coping mechanisms. Exploring aesthetic options, such as wigs, hairpieces, and stylish headwear, can also provide a boost in confidence, empowering individuals to embrace their appearance with pride.
Cultivating a positive self-image, independent of hair status, involves recognizing personal strengths, talents, and attributes that define one’s identity beyond physical appearance. By focusing on holistic well-being and self-acceptance, individuals can find strength and confidence amidst the challenges of Baldness.
When to seek professional help for hair loss
Determining the appropriate time to seek professional help for hair loss is crucial in addressing the condition effectively. Early intervention, at the first signs of unusual hair shedding or thinning, can provide a strategic advantage in mitigating Baldness and identifying underlying causes. Consulting with a dermatologist or trichologist, specialists in skin and hair health, ensures a comprehensive evaluation and tailored treatment plan.
Situations warranting immediate professional attention include rapid or patchy hair loss, scalp pain, redness, scaling, or hair loss accompanied by other health symptoms. These signs may indicate underlying medical conditions requiring prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Embracing the decision to seek professional help is a step towards empowerment, offering access to expert advice, treatment options, and support. By prioritizing hair health and seeking timely intervention, individuals can navigate the journey of hair loss with confidence and clarity.
Hair loss prevention tips
Preventing Baldness involves a multifaceted approach, integrating healthy lifestyle choices, proactive hair care, and awareness of factors that may precipitate hair loss. Maintaining a nutritious diet, rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins, supports the structural integrity and growth of hair. Staying hydrated and engaging in regular physical activity enhances overall health, indirectly benefiting hair health.
Gentle hair handling, avoiding tight hairstyles, minimizing heat styling, and using mild hair care products can reduce stress on hair follicles. Regular scalp massages, potentially incorporating essential oils, stimulate circulation and promote relaxation, offering dual benefits for hair growth.
Being mindful of stress levels and adopting effective stress management techniques can prevent stress-related hair shedding. Awareness of family history and early signs of hair thinning allows for timely intervention and preventive measures. By adopting these prevention tips, individuals can actively contribute to the health and longevity of their hair.
Conclusion
Understanding the science behind Baldness offers a pathway to empowerment, enabling individuals to navigate this complex condition with knowledge and compassion. By dispelling myths, recognizing signs and symptoms, and exploring the myriad of treatment options, individuals can approach hair loss with a proactive and informed mindset.
Embracing lifestyle changes, seeking professional guidance, and cultivating emotional resilience are pivotal steps in managing Baldness. The journey through understanding and addressing hair loss is deeply personal, yet universally shared, providing a testament to the strength found in knowledge, support, and self-acceptance.
If you found this exploration informative and enlightening, we invite you to delve deeper into related topics by exploring our article on IPL therapy and its potential role in managing various dermatological conditions, including hair loss. Thank you for joining us on this journey of knowledge and compassion.







